As you know, AMD recently introduced three new RDNA 2 GPU features: RAGE Mode, Smart Access Memory and Infinity Cache. The SAM or Smart Access Memory is a new tech feature that allows AMD CPUs to access all the VRAM in any Radeon RX 6000-series GPU.
AMD’s solution was initially supposed to work with its latest Ryzen 5000-series Zen 3 CPUs, when they are paired with any RX 6000-series GPU, on any compatible B550/X570 500-series motherboard, but later on some Motherboard vendors have also started offering support for the AMD 400-series Motherboard chipsets as well.
In a recent interview with PC World, AMD also stated that its Radeon group is working with INTEL to get this feature to work with RX 6000-series GPUs, and also on Intel’s latest compatible CPUs and motherboards.
It was also mentioned that AMD’s Ryzen group is working with Nvidia to get the new Smart Access Memory/SAM feature to work with NVIDIA GeForce GPUs. Thus, we can expect SAM to work on Nvidia GPUs as well.
In a recent statement given to GamersNexus, NVIDIA confirmed that they are indeed working on their own Smart Access Memory feature similar to what AMD has enabled on their RDNA 2 GPU lineup.
Now ASUS is the first motherboard vendor to enable the “Resizable BAR” support or AMD Smart Access Memory technology on Intel‘s platform. This has been confirmed by one official ASUS representative on Twitter.
AMD Smart Accesss Memory Support jetzt auch auf ASUS/ROG-Mainboards mit Intel Z490/H470/B460-Chipsatz. Ab Beta-BIOS 1002 bzw. 1601 pic.twitter.com/dOVf3C41rh
— Chris Wefers (@chris_wefers) December 1, 2020
The AMD Smart Access Memory (BAR) support is now accessible on all ASUS Z490, H470 & B460 motherboards. Asus has released new BIOS firmware for several 400-series motherboards that enables this Resizable BAR feature (i.e. Base Address Register). You need to download the BETA BIOS version 1002 (1601) from ASUS’s Motherboard Model support webpage.
For now, the beta 1002 BIOS supports this feature, however, a stable release will roll out soon, which would be BIOS 1003 firmware version.
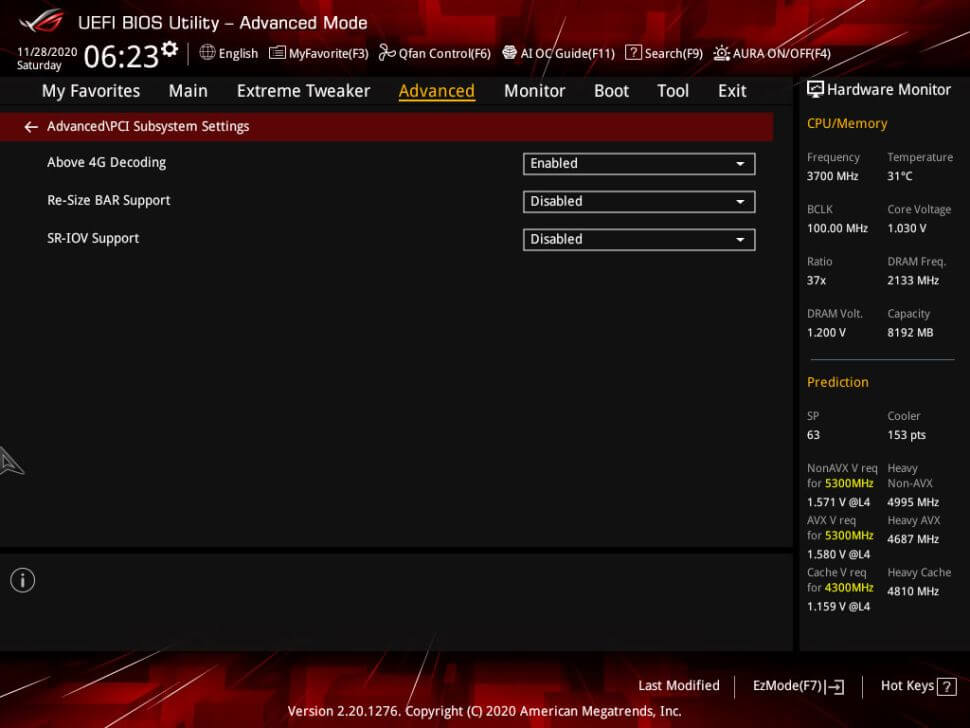
AMD Radeon RX 6000 series GPUs should now be able to take the advantage of this SAM feature, when they are paired with INTEL CPUs. Tom’s Hardware has also shown how you can enable Smart Access Memory feature through BIOS on one ASUS Z490 Motherboard, ROG Maximus XII Apex.
Enabling Smart Access Memory is pretty straightforward and easy on this board. You just have to enable the “Above 4G Decoding” and “Re-size BAR Support” settings inside the BIOS. As you can see from the screenshot posted below, both of these options are present and can be easily enabled.
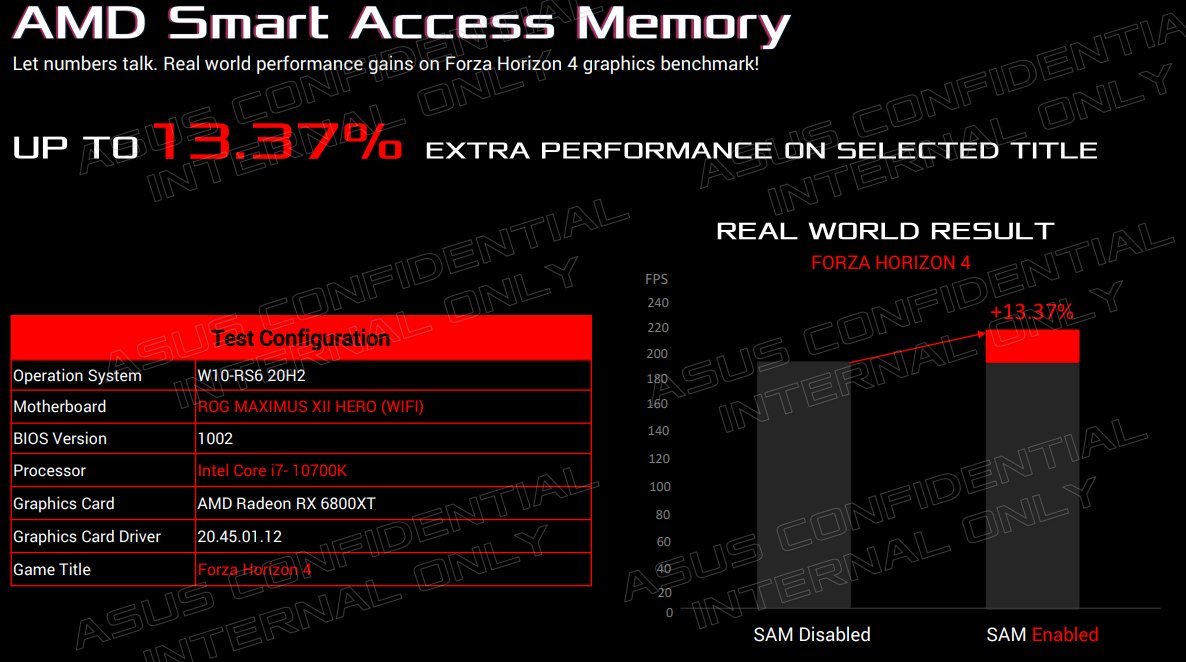
More motherboard vendors are also going to roll out Resizable BAR support on Intel platform since the technology is part of the PCIe specification after all. According to one slide shared by ASUS’s rep, Chris Wefers, we can expect at least 13.37% performance uplift in Forza Horizon 4 with BAR (Smart Access Memory) enabled, as shown below.
The testing was done on the Core i7-10700K Intel CPU platform, which was paired with the AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT GPU. The ASUS representative has confirmed that Beta BIOS is already available for the ASUS Z490, H470 and B460 motherboard chipset owners.
We can also expect NVIDIA GPUs to work on Intel platform with this BAR feature enabled. The green team has confirmed before that resizable BAR is actually a part of the PCI-Express specifications, and NVIDIA’s existing hardware fully supports this functionality.
So it is just a matter of time we see this feature getting implemented on Nvidia GPUs as well.
NVIDIA has stated this SAM feature is going to be enabled through future GPU driver/software updates, and it will be compatible with both AMD and Intel processors. This new technology feature will not require a PCIe Gen 4-compatible platform, as it will be supported by PCIe Gen 3 systems as well.
BAR basically defines how much discrete GPU memory space can be mapped. Modern PCs are typically limited to 256 MB of mapped memory.
It is typical today for a discrete graphics processing unit (GPU) to have only a small portion of its frame buffer exposed over the PCI bus. For compatibility with 32bit OSes, discrete GPUs typically claim a 256MB I/O region for their frame buffers and this is how typical firmware configures them.
A GPU, supporting resizable BAR, must ensure that it can keep the display up and showing a static image during the reprogramming of the BAR.
This feature is rather important for graphics hardware, because the PCI BARs are usually limited to 256MB while on modern cards you can easily find 4GB or more VRAM. The end result is that only a fraction of that VRAM is CPU accessible, causing a whole bunch of workarounds in the driver stack for that hardware.
AMD says that with SAM they can access all of the GPU memory, thus removing any bottlenecks. This will also allow for faster performance. In conventional Windows-based PC systems, processors can only access a fraction of graphics memory (VRAM) at once, limiting system performance.
With AMD Smart Access Memory, the data channel gets expanded to harness the full potential of GPU memory, utilizing the bandwidth of PCI Express to remove the bottlenecks and increase performance.
To reiterate some of the main points, AMD’s new Smart Access Memory feature will boost the overall gaming performance by optimizing the data transfer between the CPU and the GPU.
What this basically means is that the Radeon RX 6000 GPUs can now work and operate in tandem with AMD’s Ryzen 5000-series processors, provided you use a 500-series compatible motherboard, through this new Smart Access Memory feature.
Smart Access Memory aims at optimizing both the GPU and CPU to offer the best possible performance when they operate in tandem.
According to the concept, once you enable the Smart Memory Access feature in the RX 6000 card’s VBIOS and the motherboard BIOS, both the CPU and GPU will gain full access to each other’s memory. Doing this will maximize data transfer and performance between the CPU and the GPU’s VRAM.
Smart Access Memory helps boost performance by enabling faster data transfer speeds between the CPU and GPU. And by pairing this efficient data transfer smart access feature with the new 128MB Infinity Cache might help boost the throughput between the CPU and the GPU as well.
The new Infinity Cache takes advantage of the GPU’s data paths to maximize performance while minimizing the data movement and power within the GPU itself.
According to AMD, Infinity Cache delivers a 10% increase in power efficiency and it also doubles the bandwidth (almost 117% increase), all at a lower power than traditional memory.
Infinity Cache is based on the Zen CPU’s L3 cache design. Infinity Cache boosts performance-per-clock scaling as frequency increases largely because the GPU is now less constrained by external memory bandwidth limits. The Infinity Cache also boosts ray tracing performance, as more of the data set is kept closer to the compute units to feed.
It remains to be seen how much of a performance boost this SAM feature gives on AMD, Intel and Nvidia’s hardware.
Stay tuned for more!
Hello, my name is NICK Richardson. I’m an avid PC and tech fan since the good old days of RIVA TNT2, and 3DFX interactive “Voodoo” gaming cards. I love playing mostly First-person shooters, and I’m a die-hard fan of this FPS genre, since the good ‘old Doom and Wolfenstein days.
MUSIC has always been my passion/roots, but I started gaming “casually” when I was young on Nvidia’s GeForce3 series of cards. I’m by no means an avid or a hardcore gamer though, but I just love stuff related to the PC, Games, and technology in general. I’ve been involved with many indie Metal bands worldwide, and have helped them promote their albums in record labels. I’m a very broad-minded down to earth guy. MUSIC is my inner expression, and soul.
Contact: Email